Mapping frequencies.
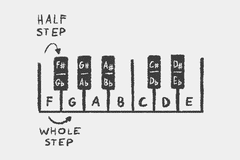
Western music theory generally divides an octave into a series of twelve notes, called the chromatic scale.
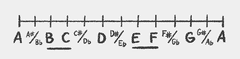
A A♯/B♭ B C C♯/D♭ D D♯/E♭ E F F♯/G♭ G G♯/A♭
The chromatic scale consists of 12 notes in total: 7 natural notes and 5 enharmonic notes.
Natural notes are A B C D E F G
Enharmonic notes are natural notes highered or lowered by a half step: A♯/B♭ C♯/D♭ D♯/E♭ F♯/G♭ G♯/A♭.
B♭ is pronounced B Flat.
They are the same note.
Interval Exception: the BC-EF-Rule
A special rule is the BC-EF-Rule: there are no enharmonic notes between B and C and E and F.
Scale Formulas
Scales are found using patterns of whole and half steps.
W = Whole Step H = Half Step
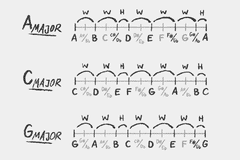
Major Scale
W W H W W W H
The most commonly used Western music scale. Also called Ionian mode.
Natural Minor Scale
W H W W H W W
Also called Aeolian mode.

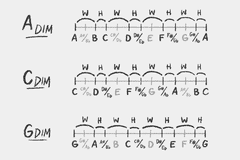
Diminished Scale
W H W H W H W H
A whole step / half step pattern.
incoming(1) | circle of fifths