Fundamentals of music theory.
"Theory derives from the Ancient Greek word theoria (θεωρία), meaning "to look at". Thus Music Theory is making music visible."
Similar to the geometry of the color circle, music can be arranged cyclically and put into relationships forming patterns. These patterns are known as scales, chords and progressions. They are used to make intentional music.
music terminology
- Pitch: The lowness or highness of a tone; the frequency of a sound wave.
- Interval: The difference in pitch between two notes, also called a half step.
- Whole Step: Two half steps.
- Octave: Two pitches that are either the double or the half the frequency of one another.
- Temperament: Refers to musical tuning systems, determining the prceise size of intervals.
- Transposition: raising or lowering the overall pitch range, but preserves the intervallic relationships of the original scale.
- Melody: A series of tones perceived as an entity sounding in succession that typically move toward a climax of tension and then resolve to a state of rest. The basic elements of melody are pitch, duration, rhythm and tempo. It is the horizontal aspect of music.
- Harmony: The vertical aspect of music. Multiple melodic lines and separate, independent voices interweaving in polyphony.
- Timbre: The principal phenomenon that allows us to distinguish one instrument from another when both play at the same pitch and volume. Also called tone color.
- Texture: The overall quality of a sound in a composition defined by the combination of the melodic, rhythmic and harmonic features. Often described in regard to density and range between the lowest and highest pitches or the number of voices.
- Chord Progression: A series of chords.
- Arpeggio: A chord broken and played as separate notes.
scales
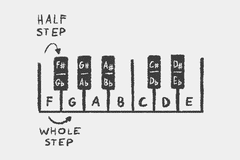
Western music theory generally divides an octave into a series of twelve notes, called the chromatic scale.
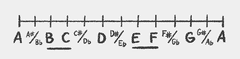
A A♯/B♭ B C C♯/D♭ D D♯/E♭ E F F♯/G♭ G G♯/A♭
The chromatic scale consists of 12 notes in total: 7 natural notes and 5 enharmonic notes.
Natural notes are A B C D E F G
Enharmonic notes are natural notes highered or lowered by a half step: A♯/B♭ C♯/D♭ D♯/E♭ F♯/G♭ G♯/A♭.
B♭ is pronounced B Flat.
They are the same note.
Interval Exception: the BC-EF-Rule
A special rule is the BC-EF-Rule: there are no enharmonic notes between B and C and E and F.
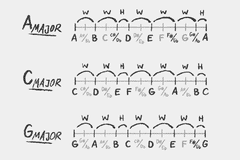
Scale Formulas
Scales are found using patterns of whole and half steps.
W = Whole Step H = Half Step
Major Scale
W W H W W W H
The most commonly used Western music scale. Also called Ionian mode.
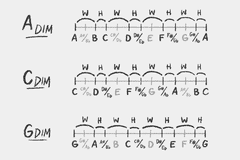
Natural Minor Scale
W H W W H W W
Also called Aeolian mode.

Diminished Scale
W H W H W H W H
A whole step / half step pattern.
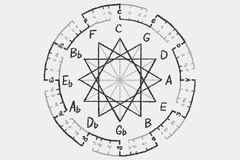
circle of fifths

To describe musical relationships between the pitches of the chromatic scale, they can be organised in a circle of perfect fifths, or seven half steps.
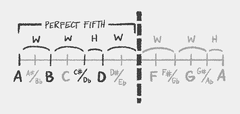
It also describes the relationship that different scales have to one another and often showns the major, minor and diminished scales.
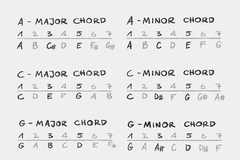
chords
A chord is a harmonic set of three or more notes heard as if sounding simultaneously. The most frequent chords are called triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: the root note, the third and the fifth.
guitar
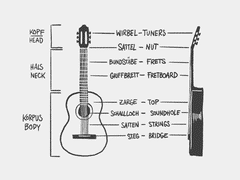
The guitar consists of the body, the neck and the head.
Intonation - Bundrein
The pitch accuracy of all possible notes on the fretboard. Check by playing an open string and then playing the note on the 12th fret of the same string. The note should be an octave - the double frequency of the open pitch.
incoming(2) | review 2023 | cmus